
Friday March 6, 2020 ~ INTERNATIONAL
by Mary Brooke, B.Sc. ~ West Shore Voice News
“Slowing down the epidemic saves lives, and it buys time for preparedness and for research and development,” said the Director-General of the World Health Organization (WHO), Dr Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, today March 6.
In his remarks two days ahead of International Women’s Day — which he opened with an explanatory statement about how many women around the world are disadvantaged in terms of access to health care.
Then he continued with the grim facts of the continuing COVID-19 situation which now tallies almost 100,000 confirmed cases globally.
“Every day we slow down the epidemic is another day governments can prepare their health workers to detect, test, treat and care for patients,” the Director-General said.
“Every day we slow down the epidemic is another day closer to having vaccines and therapeutics, which can in turn prevent infections and save lives,” he said.
Last month WHO convened a meeting of more than 400 scientists to identify research priorities. Today WHO published a Research & Development roadmap which distills those ideas into a core group of priorities in nine key areas including the natural history of the virus, epidemiology, vaccines, diagnostics, therapeutics, clinical management, ethical considerations, social sciences and more.
WHO has been monitoring the potential risk of a disruption to medicines supplies as a result of the COVID-19 epidemic. China — where most of the COVID-19 cases have and are occurring — is a major producer of active pharmaceutical ingredients and the intermediate products that are used to produce medicines in other countries.
WHO has received applications for review and approval of 40 diagnostic tests, 20 vaccines are in development and many clinical trials of therapeutics are underway.
WHO has focused on the most essential medicines that are critical for primary health care and emergencies, including antibiotics, pain killers, and treatments for diabetes, hypertension, HIV, tuberculosis, and malaria.
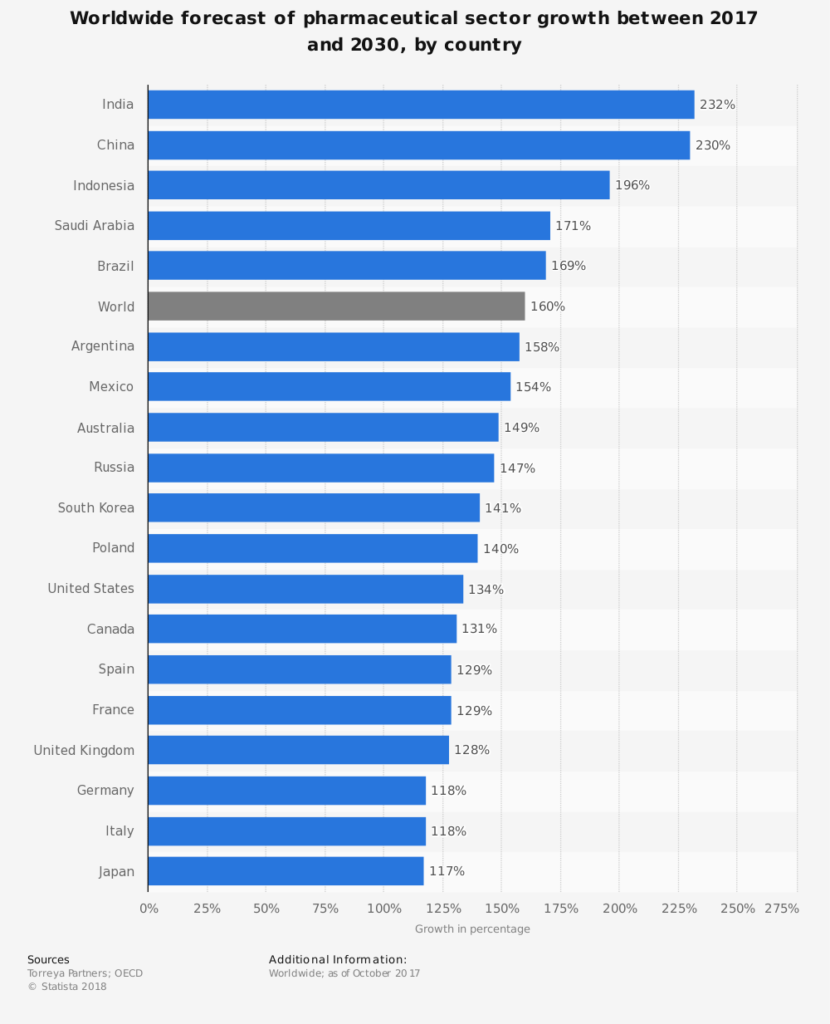
Back in November 2017 a paper was published by Statista.com showing a worldwide forecast of pharmaceutical sector growth between 2017 and 2030, sorted by select country. That was before COVID-19. The forecast back then predicted the pharmaceutical sector worldwide would grow by 160%, with the biggest growth forecast given for India with 232%. The impediment to China right now for continuing as a lead producer of pharmaceutical components may allow other countries to get further into that manufacturing sector.
======= About the WHO Director-General
Dr Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus was elected as WHO Director-General for a five-year term by WHO Member States at the Seventieth World Health Assembly in May 2017.
He is the first WHO Director-General to have been elected from multiple candidates by the World Health Assembly, and is the first person from the WHO African Region to serve as WHO’s chief technical and administrative officer.
Immediately after taking office on 1 July 2017 Dr Tedros outlined five key priorities for the Organization: universal health coverage; health emergencies; women’s, children’s and adolescents’ health; health impacts of climate and environmental change; and a transformed WHO.


